What Is AWS Cost Optimization?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is the world’s leading cloud computing platform, providing hundreds of services covering compute, storage, networking, and platform as a service (PaaS) offerings such as managed databases and container orchestration.
Optimizing AWS costs involves monitoring and analyzing your usage, identifying opportunities to reduce costs, and implementing recommended actions.
Most Amazon services are based on compute resources provided by the Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), so the cost of EC2 instances is probably a central factor in your AWS costs. Many optimization strategies involve reducing the cost of EC2 instances—for example by switching instances from on-demand pricing to lower-cost spot instances or reserved instances, or applying savings plans which can reduce costs across your Amazon account.
This is part of an extensive series of guides about FinOps.
In this article:
- Why Is AWS So Expensive?
- Pillars of AWS Cost Optimization
- 3 AWS Cost Optimization Tools
- 12 AWS Cost Optimization Best Practices
Why Is AWS So Expensive?
The AWS cloud provides over 200 services. Cloud resources are dynamic and cost can be unpredictable and difficult to manage.
Here are the main causes of waste and high costs on AWS:
- Compute instances on services like Amazon EC2 are under-utilized, meaning you are paying for instances you don’t actually need.
- Unused EBS volumes, snapshots, load balancers, or other resources are not in use but still incurring costs.
- Spot instances or reserved instances are not used when they are applicable – these types of instances can provide discounts of 50-90%.
- Savings Plans are not used – these can help you save on compute costs by committing to a minimum total spend on AWS.
- Auto scaling is not implemented or not optimal – for example, as demand increases, you scale up too much (adding redundant resources).
Pillars of AWS Cost Optimization
Here are five cost optimization pillars you can apply to most environments:
- Right size – the resources you provision must match your requirements and needs. For example, you should provision CPU, storage, network throughput, and memory for computing.
- Increase elasticity – traditionally, IT hardware is rarely turned off. The cloud model enables you to optimize costs to meet dynamic needs, turning resources off when you no longer need them.
- Leverage the right pricing model – AWS offers various pricing models, including on-demand pricing, Spot Instances, and Reserved Instances. The pricing model you choose should allow you to optimize costs according to your workload’s needs. For example, reserved instances are ideal for predictable workloads.
- Optimize storage – AWS offers several storage tiers, each providing different performance at different costs. You can optimize storage and maintain the required performance and availability by identifying the appropriate destination for specific data types. For example, for lower performance requirements, you can use Amazon EBS Throughput Optimized HDD (st1), which costs less than General Purpose SSD (gp2).
- Measure, monitor, and improve – since cloud environments are dynamic, you need to establish measurements and monitor for accurate visibility and continuous costs optimization. You can set this up by defining and enforcing cost allocation tagging. You should define metrics, set specific targets, and review the information regularly. Use training, visualization, and incentives to help teams architect for cost, and assign optimization responsibilities to certain individuals or teams.
3 AWS Cost Optimization Tools
Here are several AWS cost optimization tools available free from Amazon:
To learn other ways to reduce your cloud costs, see our detailed guide to AWS cost savings
1. AWS Cost Explorer
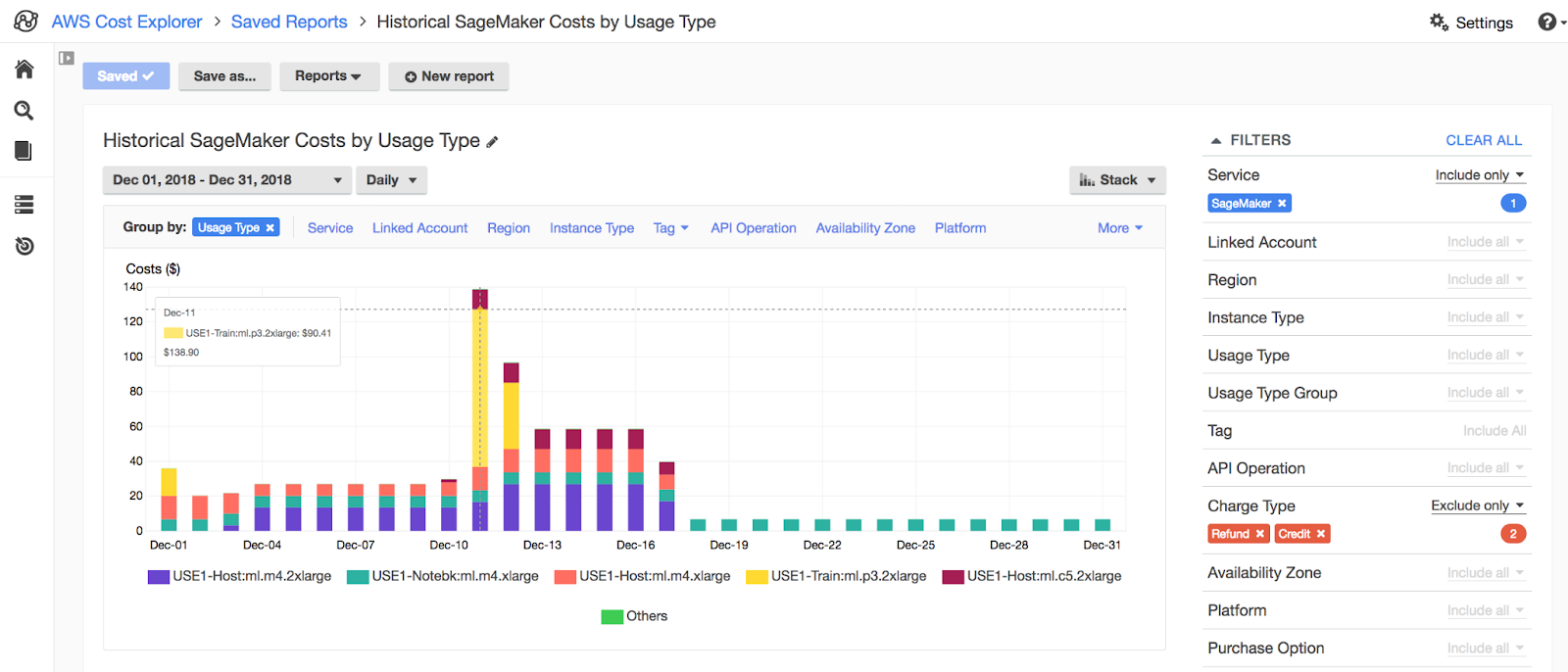
The Cost Explorer interface enables you to view costs, usage and return on investment (ROI) for AWS services. The interface displays data for the past 13 months and can help you forecast your future spend. You can use the interface to create customized views, which can help further analyze your AWS costs and also identify certain areas for improvement. Additionally, the AWS Cost Explorer provides an API, which enables you to access data through your existing analytics tools.
Learn more in our detailed guide to the AWS Cost Explorer
2. AWS Budgets
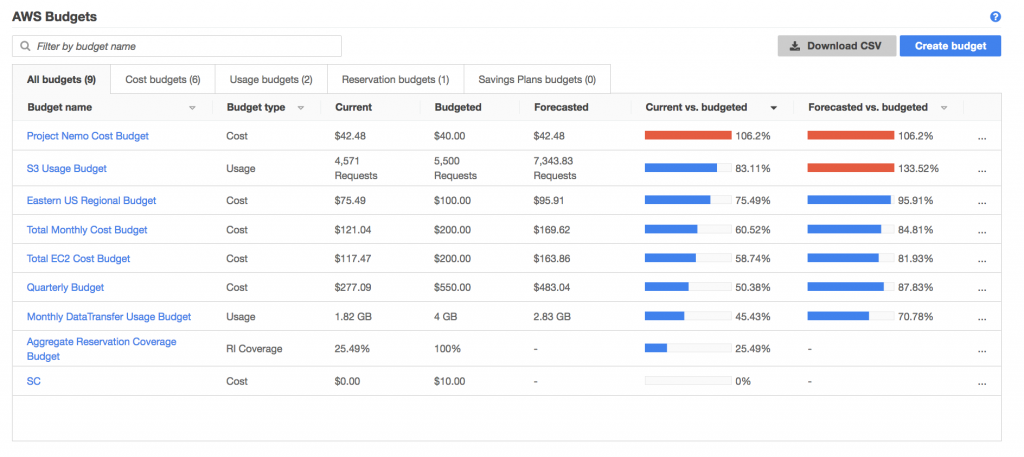
AWS Budgets can help you set and enforce budgets for each AWS service. When budgets are exceeded or reached, you can receive messages or emails from the Simple Notification Service (SNS). You can define an overall cost budget or connect a budget to certain data points, including data usage or the number of instances. The tool provides dashboard views similar to those generated by the Cost Explorer, displaying how each service is used compared to its budget.
Learn more in our detailed guide to AWS Budgets
3. AWS Pricing Calculator
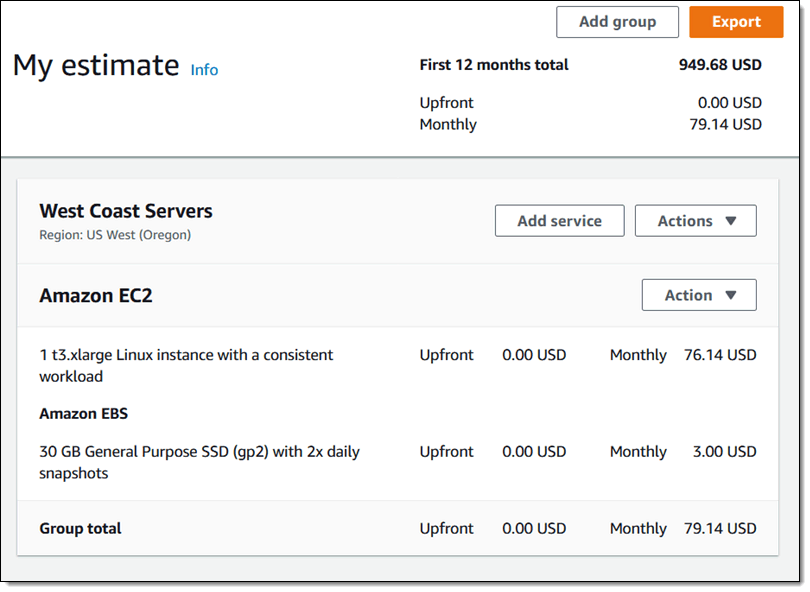
AWS Pricing Calculator enables you to estimate the cost of use cases on AWS. It lets you generate monthly cost estimates for all regions supported by a certain service. You can model a solution before building it, explore the pricing points and calculations of your estimate, as well as find available instance types and contract terms that meet your requirements. This can help you make informed decisions, plan your AWS cost and usage, as well as estimate the costs of setting up a new set of instances and services.
Read more in our guide to AWS Pricing Calculator
12 AWS Cost Optimization Best Practices
The following best practices can help you optimize and reduce your AWS costs.
1. Choose the Appropriate AWS Region
To use the AWS Management Console, CLI or SDK, you must first choose a region. Most users base this decision on distance. However, the AWS region you choose also affects costs, latency and availability. Here are several aspects to consider when choosing the right AWS region for your project:
-
- Costs—each AWS region is priced differently. You can view official on-demand pricing on the AWS site, but make sure to use the cost calculator to estimate your costs when using a certain region.
- Latency—regions with smaller latency can help make the application more accessible to a certain group of users.
- Service availability—not all AWS services are made available to all regions. Before choosing a particular region, make sure the target AWS service is available in this region.
- Availability—using multiple AWS regions can improve availability and enable you to create a separate disaster recovery site.
- Data sovereignty—when you store data in a specific geographical location, your organization must comply with that location’s legal requirements for the data. This is an important consideration for locating your sensitive data.
When accounting for all above aspects, you can prioritize them to choose the most important aspect and let it guide you as you choose a region.
2. Create Schedules to Turn Off Unused Instances
When optimizing your AWS costs, you must pay attention to unused instances and shut them down. Here are several practices to consider:
- Shut down unused instances at the end of a working day or during weekends and vacations.
- When optimizing non-production instances, you should prepare on and off hours in advance.
- Evaluate usage metrics and then decide when instances are frequently used. You can then implement more accurate schedules. Alternatively, you can apply an always-stopped schedule, which you can disrupt when providing access to these instances.
- Determine whether you are paying for EBS quantities as well as other relevant elements while your instances are not in use.
Read more in our guide to AWS Cost Anomaly Detection
3. Identifying Under-Utilized Amazon EC2 Instances
The AWS Cost Explorer helps you visualize and manage the cost of Amazon services. The tool provides a Resource Optimization report, which shows idle or under-utilized EC2 instances. You can lower your costs by stopping or scaling down these instances.
Here are three tools to help you to stop wasting money on low utilization EC2 instances:
- AWS Instance Scheduler – a pre-integrated Amazon solution you can use to stop instances automatically on a predetermined schedule, for example outside business hours.
- AWS Operations Conductor – automatically resizes EC2 instances based on recommendations provided by Cost Explorer.
- AWS Compute Optimizer – provides recommendations about the most appropriate instance type for each workload. This goes beyond scaling down within a group of instances. It offers recommendations for downsizing instances across groups, as well as recommendations for upsizing to eliminate performance bottlenecks, and recommendations for EC2 instances in an Auto Scaling group.
4. Reducing EC2 Costs with EC2 Spot Instances
Amazon EC2 spot instances are an important option for reducing AWS costs. Spot instances provide savings of up to 90% compared to normal on-demand prices.
Spot instances are Amazon’s way to sell off spare EC2 capacity. They can significantly reduce Amazon EC2 costs by allowing you to request the same EC2 instances, when they are in low demand, at a significantly discounted price.
The downside of spot instances is that they are unreliable—if Amazon needs to reclaim the capacity for on-demand or reserved users, it terminates the instance with a two-minute warning. Amazon has recently introduced “rebalancing signals” which may provide earlier warning of spot instance termination, but this is not guaranteed. Another option to improve reliability is to run spot instances in an Auto Scaling Group (ASG) together with regular on-demand instances. This way at least some of the capacity in the group is guaranteed to remain available.
You can overcome these challenges and use spot instances even for mission critical or production workloads that cannot tolerate interruption with cloud optimization tools like Elastigroup from Spot. Elastigroup provides AI-driven prediction of spot instance interruptions, and can perform automated rebalancing of workloads, to eliminate the “surprise factor” and risk of spot instance termination.
5. Optimizing EC2 Auto Scaling Groups (ASG) Configuration
An ASG is a collection of Amazon EC2 instances, treated as a logical group for automatic scaling and management purposes. ASGs can take advantage of Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling features, such as health checks and custom scaling policies based on application metrics or preset schedules. You can dynamically add or remove EC2 instances from an ASG based on predetermined rules or dynamically, in response to application loads.
ASGs let you scale your EC2 fleets up or down as needed to conserve costs. You can view scaling activity by using the describe-scaling-activity CLI command, or the Auto Scaling Console. By optimizing scaling policies, you can reduce costs both when scaling up and down:
- When scaling up—try to add instances less aggressively, monitoring to see that application performance is not affected
- When scaling down—try to reduce instances to the minimum necessary to maintain current application loads
Here too, a tool like Elastigroup can help by exactly matching scaling events to application requirements, ensuring there are no wide margins that waste capacity. This can also save your team time, because there is no need to constantly monitor and fine tune auto scaling policies.
Learn more about using Elastigroup to optimize EC2 auto scaling
6. Using or Selling Under-Utilized Reserved Instances
An Amazon Reserved Instance (RI) lets you commit to using an instance for periods of one or three years, providing a discount of up to 72%. There are several options you need to consider when committing to reserved instances:
- Standard or Convertible—you can resell standard RIs on the AWS RI Marketplace if you no longer need them, but you cannot change the type of instance group. You cannot resell convertible RIs, but you can change them to any instance type or family.
- Regional or Zonal—regional RIs let you move the instance to a different zone, and also allow you to change to an equivalent instance size within the same family, but do not guarantee capacity. Zonal RIs guarantee capacity, without letting you change zone or instance type.
- Payment options—you can decide whether to pay upfront for the commitment period, pay some of the amount upfront, or pay everything on an ongoing basis. Upfront payment grants larger discounts.
- Service support—you can now use RIs for EC2, RDS, Redshift, ElastiCache and DynamoDB.
Because RIs represent a long-term commitment, you may find yourself with unused reserved instances. This is why initial planning is important:
- If you are sure you’ll need RI capacity during the commitment period, opt for Convertible instances, so you can reuse the instance for other workloads if necessary.
- If there is a chance you won’t need some of the RIs for the entire commitment period, opt for Standard instances and sell them on the marketplace if needed.
Here too, automated optimization tools can be useful. Eco from Spot can help you automatically adjust your portfolio, to offload unused reserved instances, or relocate workloads from expensive on-demand instances.
Learn how to use Eco from Spot to optimize the use of EC2 reserved instances
7. Leveraging Compute Savings Plans to Reduce Compute Costs
The Savings Plan is a flexible pricing model that lets users use EC2, Lambda, and Fargate at a lower cost, by committing to a continuous usage, measured in terms of USD per hour, for a period of 1 or 3 years. For example, a one-year Savings Plan with no upfront payment plan grants a discount of up to 54%.
Savings Plans apply to compute instances regardless of size, Auto Scaling Group, Availability Zone, or region. You can use AWS Cost Explorer to select the right options for your plan, based on an analysis of recent utilization.
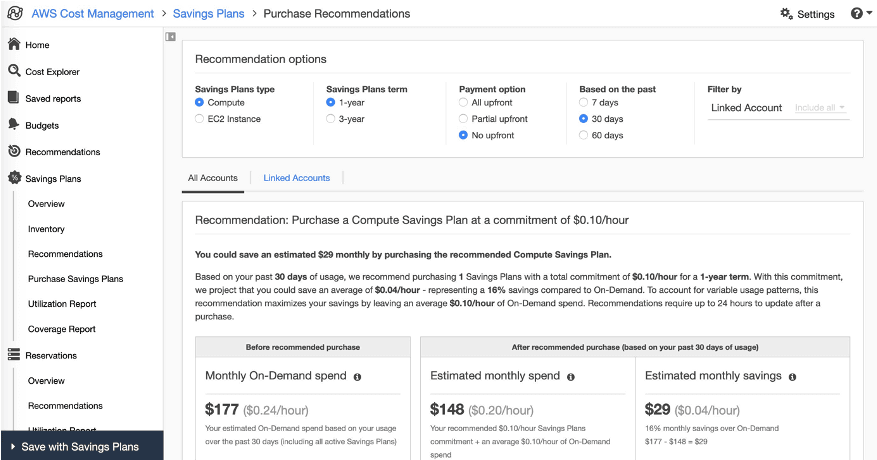
While Cost Explorer provides useful recommendations, your usage of Amazon services is dynamic, and there is a need to continuously manage and optimize your commitments. A cloud optimization tool like Eco constantly evaluates cloud usage and manages Savings Plans and reserved instance lifecycles automatically, to ensure you make the best use of long term commitments and achieve maximal discounts.
Learn how to use Eco from Spot to optimize the use of EC2 savings plans
8. Monitor the Use of Storage and Delete Unused EBS Volumes
Monitoring can help you track actual usage and identify pricing patterns. AWS lets you monitor S3 usage via the S3 Analytics tool, which evaluates storage access patterns on a specific object dataset for a duration of 30 days or more.
The S3 Analytics tool offers recommendations that can help you leverage S3 Infrequently Accessed (S3 IA), AWS Glacier, or AWS Glacier Deep Archive for cost reduction.
You can then use lifecycle policies to automate the transfer of objects into a lower cost storage tier. Alternatively, you can use S3 Intelligent-Tiering for automatic analysis and transfer of objects with unknown or dynamic usage duration into a relevant storage tier.
In addition, a great way to save storage is to delete unused Elastic Block Storage (EBS) volumes – managed disk drives you can attach to EC2 instances. Even after the EC2 instance shuts down, EBS volumes can continue operating and incur costs.
Make sure teams are aware that when they use EBS volumes, they should select the option to Delete on termination. This will ensure that the EBS volume is deleted when the EC2 instance is terminated. If this was not done, look for EBS volumes that are marked as available—you can do this via Amazon CloudWatch or AWS Trusted Advisor, and clean them up automatically using a Lambda function.
9. Identifying and Deleting Orphaned Snapshots
When you terminate an EC2 instance, the associated EBS volume is also deleted by default. However, it’s easy to forget that snapshots you created as backups of those EBS volumes are still in S3, and you’re still paying an ongoing monthly fee to store them.
EBS backups are usually incremental, so each additional snapshot takes up limited storage space. However, if you perform frequent snapshots and have a high retention period, even this small incremental addition can add up over time.
Because most snapshots use data from the initial snapshot of the entire EBS volume, it is important to track down and delete the initial snapshot, if it is not needed. This can save much more storage space than deleting numerous incremental snapshots.
It is best to set up automated lifecycle management of EBS snapshots, via Amazon Data Lifecycle Manager, to ensure that you do not maintain snapshots for longer than needed.
10. Deleting Idle Load Balancers and Optimizing Bandwidth Use
Check your Elastic Load Balancing configuration to see which load balancers are not currently used. Every load balancer incurs ongoing costs. If your load balancer doesn’t have any backend instances associated with it, or network traffic is very low, it is not being used effectively and is wasting resources.
You can use AWS Trusted Advisor to identify load balancers with a low number of requests (a good rule of thumb is less than 100 requests in the last 7 days). Reduce costs by removing idle load balancers—you can track overall data transfer costs with Cost Explorer.
Another way to reduce costs, if you have high data transfer costs from EC2 to the public web, is to use Amazon CloudFront. CloudFront is a Content Delivery Network (CDN), which lets you cache web content in multiple edge locations around the world. This can significantly reduce the bandwidth required to serve spikes in traffic.
11. Charging Back Amazon Costs to Internal Users with Enterprise Billing Console
AWS Enterprise Billing Console is a new service that lets you manage chargebacks—billing Amazon services to units in your organization, or to third parties. Within an organization, this allows you to create accountability by billing each department or business unit, according to the cost of services they actually use.
The Enterprise Billing Console lets you allocate your costs across accounts, and use the concept of billing groups. Billing groups let you apply customized pricing plans to each department or business unit. Set up Cost and Usage (CUR) reports for each of your billing groups, and perform margin analysis to calculate savings for each group as a result of cost optimizations.
Another feature of the console is dashboard graphs, which offer default views of your overall spending, as well as month-to-date spend and service consumption by each group.
Spot Eco can be used by enterprises looking to easily manage cost, internal billing and showback for various business units.
Related content: Read our guide to AWS cost management
12. Automatically Optimizing Cloud Costs with Spot
While AWS offers Savings Plans, RIs and spot instances for reducing EC2 cost, these all have inherent challenges:
- Spot instances can be 90% less expensive than on-demand instances, however, as spare capacity, AWS can reclaim those instances with just a two minute warning, making them less than ideal for production and mission-critical workloads.
- AWS Savings Plans and RIs can deliver up to 72% cost savings, but they do create financial lock-in for 1 or 3 years and if not fully utilized can end up wasting money instead of saving it.
Spot addresses these challenges, allowing you to reliably use spot instances for production and mission-critical workloads as well as enjoy the long-term pricing of RIs without the risks of long-term commitment.
Key features of Spot’s cloud financial management suite include:
- Predictive rebalancing—identifies spot instance interruptions up to an hour in advance, allowing for graceful draining and workload placement on new instances, whether spot, reserved or on-demand.
- Advanced auto scaling—simplifies the process of defining scaling policies, identifying peak times, automatically scaling to ensure the right capacity in advance.
- Optimized cost and performance—keeps your cluster running at the best possible performance while using the optimal mix of on-demand, spot and reserved capacity.
- Enterprise-grade SLAs—constantly monitors and predicts spot instance behavior, capacity trends, pricing, and interruption rates. Acts in advance to add capacity whenever there is a risk of interruption.
- Serverless containers—allows you to run your Kubernetes and container workloads on fully utilized and highly available compute infrastructure while leveraging spot instances, Savings Plans and RIs for extreme cost savings.
- Intelligent and flexible utilization of AWS Savings Plans and RIs—ensures that whenever there are unused reserved capacity resources, these will be used before spinning up new spot instances, driving maximum cost-efficiency. Additionally, RIs and Savings Plans are fully managed from planning and procurement to offloading unused capacity when no longer needed, so your long-term cloud commitments always generate maximum savings.
- Visibility and recommendations—lets you visualize all your cloud spend with the ability to drill-down based on the broadest range of criteria from tags, accounts, services to namespaces, annotations, labels, and more for containerized workloads as well as receive cost reduction recommendations that can be implemented in a few clicks.
Learn more about Spot’s cloud financial management solutions
See Additional Guides on Key FinOps Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of FinOps.
AWS High Availability
Authored by NetApp
- Understanding AWS High Availability: Compute, SQL and Storage
- AWS Availability Zones, Regions, & Placement Groups Explained
- AWS Data Loss Prevention: Tools and Strategies
AWS Pricing
Authored by Spot
- AWS Pricing: 5 Models & Pricing for 10 Popular AWS Services
- Fargate vs. EC2: What is the difference and which is best for ECS?
- Run an EMR Cluster on Spot Instances in 5 Steps
Azure Cost Optimization
Authored by Spot.io
