What is AWS CI/CD?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides CI/CD tools designed to accelerate the software development cycle. The term “CI/CD” encompasses the following aspects:
- Continuous integration (CI) refers to a development process that involves regularly pushing code into repositories like GitHub and AWS CodeCommit. Each code push triggers an automated build, closely followed by tests.
- Continuous delivery (CD) refers to a deployment process that involves deploying artifacts to staging environments, testing environments, and production environments. DevOps teams can fully automate the CD process or add approval stages at critical points.
CI helps developers discover code issues early in the development process. Early discovery enables developers to improve the quality of their code and reduce the time spent validating and releasing software updates. CD helps developers ensure they always have a deployment-ready build artifact that has passed testing standards.
Continuous delivery vs. continuous deployment
The acronym CD is often used to refer interchangeably to continuous delivery and continuous deployment. However, there are key differences between the two processes, including:
- Continuous deployment fully automates the software release cycle—a continuous deployment process automatically deploys revisions to a production environment without requiring explicit approval. The result is a continuous customer feedback loop that starts early in the product lifecycle.
- Continuous delivery ensures each change is ready to go to production—a continuous delivery process focuses on preparing new code for deployment. The focus here is on preparation with fully automated processes that get new features and updates into the hands of users quickly and safely.
This is part of a series of articles about CI/CD
In this article, you will learn:
- Services You Can Use to Build a AWS CI/CD Pipeline
- Tutorial: Create a Simple CI/CD Pipeline in AWS
- AWS CI/CD with Spot
Services You Can Use to Build a AWS CI/CD Pipeline
AWS CodePipeline
AWS CodePipeline offers a continuous delivery (CD) service for quick and reliable application updates. Based on predefined release process models, the service can build, test, and deploy your code. You can leverage AWS CodePipeline to increase the speed of updates delivery while maintaining reliability.
AWS CodePipeline lets you easily build an end-to-end solution using plugins built for popular third-party services, such as GitHub. Alternatively, you can integrate custom plugins into various stages of the release process. AWS CodePipeline bills you only for what you use, without charging any upfront fees or asking for long-term commitments.
AWS CodeDeploy
AWS CodeDeploy automates the deployment of code to Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon ECS tasks, AWS Fargate, AWS Lambda, as well as machines running on-premises. You can use AWS CodeDeploy to release new features and avoid downtime during application deployment. Additionally, the service can automatically update applications without the risks associated with error-prone manual deployments.
Amazon EC2
Amazon EC2 offers the use of cloud-based virtualized servers, commonly known as instances. EC2 lets you configure and scale compute capacity easily to meet changing demand and requirements. The service is seamlessly integrated with other AWS offerings.
AWS CodeCommit
AWS CodeCommit offers fully-managed source control. The service lets you host highly scalable and secure private Git repositories within the AWS cloud. CodeCommit offers secure cloud storage for source code and binaries.
Tutorial: Create a Simple CI/CD Pipeline in AWS
These instructions are abbreviated from the AWS CodePipeline official tutorial. The tutorial shows how to use CodePipeline to deploy code changes to an Amazon EC2 instance. It shows how to create an Amazon CodeCommit repository to store your code and uses CodeDeploy to deploy the changes.
1. Create a CodeCommit Repository
Let’s see how to create a CodeCommit repository and push code to it from your local repository:
- Access the CodeCommit console. You can use this URL: https://console.aws.amazon.com/codecommit/.
- Click Region and select an AWS Region—this is where Amazon will create your code repository and CI/CD pipeline.
- Navigate to the Repositories page and click Create repository. Type a name for the repo and click Create.
- Keep the new repo open in the browser, click Clone URL at the top right of the screen, and select Clone SSH, to copy the URL to your CodeCommit Git repository.
- Open a terminal, create a local directory that should store your local repo, and run the following command. Replace “SSH access URL” with the address you copied from the console:
git clone <SSH access URL> - Finally, add some sample code. Download this file from Amazon: SampleApp_Linux.zip and unzip it into your local repo.
2. Create an Application in CodeDeploy
Amazon CodeDeploy uses the concept of an application—this represents the application you are developing and need to deploy. Let’s create a sample application in CodeDeploy:
- Access the CodeDeploy console. You can use this URL: https://console.aws.amazon.com/codedeploy.
- Click Applications > Create application, and type a name for your application.
- Under Compute Platform, select EC2/On-premises, and click Create application.
3. Create an EC2 Linux Instance and Install the CodeDeploy Agent [P2]
AWS lets you install a CodeDeploy agent that can use an IAM role to deploy your application. Here is how to create an instance role:
- Go to the IAM console using this URL: https://console.aws.amazon.com/iam/.
- Go to the IAM console dashboard and choose the Roles option.
- Select Create role.
- Find the Select type of trusted entity option and choose AWS service.
- Locate the Choose a use case option and choose EC2.
- When asked to Select your use case, opt for EC2. Then, choose Next: Permissions.
- Find and choose the policy called “AmazonEC2RoleforAWSCodeDeploy”.
- Select the Next: Tags option.
- Select the Next: Review option.
- Type a descriptive name for your new role. For example,
myEC2InstanceRole. - Choose the Create role option.
4. Create Your First Pipeline in CodePipeline
We now have a repo and an application. Let’s put it all together by creating a pipeline that accepts code changes and automatically deploys the application:
- Access the CodePipeline console. You can use this URL: https://console.aws.amazon.com/codesuite/codepipeline/home.
- Click Create pipeline.
- In Step 1, type a pipeline name. Under Service role, select New service role. Click Next.
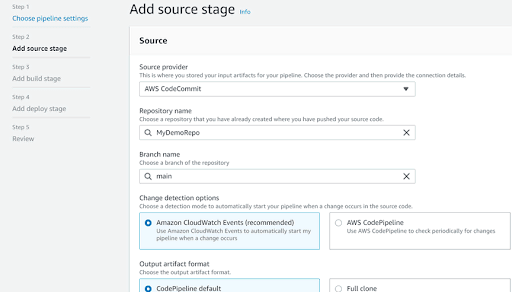
- In Step 2, under Source provider, select CodeCommit. Under Repository name, choose the CodeCommit repository you created earlier, and then choose
mainunder Branch name. Click Next.
Image Source: AWS - In Step 3, choose Skip build stage, and click Next.
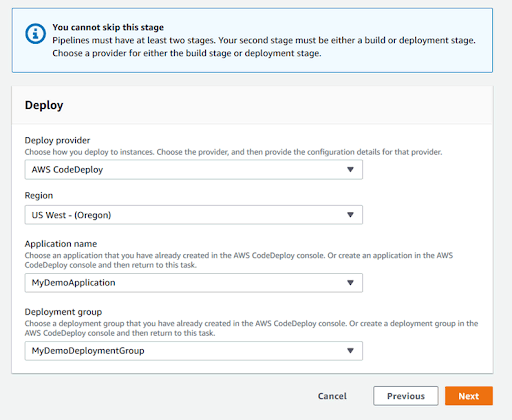
- In Step 4, under Deploy provider, select AWS CodeDeploy, and select the application you created earlier. Under Deployment group, choose the only available deployment group, and click Next.
Image Source: AWS - In Step 5, review the options you selected and click Create pipeline.
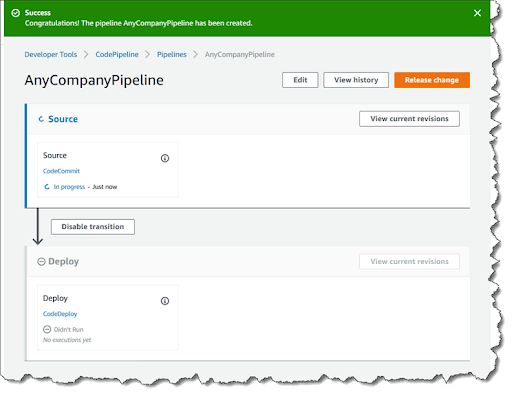
That’s it! Your automated CI/CD pipeline immediately starts running. To test it, commit the sample code you added to your local repository. Here is what happens next:
- Your CodePipeline downloads the code from the CodeCommit repository
- CodeDeploy starts an EC2 instance and deploys the application to it.
- You can see the progress of the deployment in the CodeDeploy console.
Image Source: AWS
AWS CI/CD with Spot
Continuous Delivery has entered a new phase as more and more applications are migrating to microservices, with Kubernetes as the container orchestrator of choice for many. Kubernetes enables agility and faster software development cycles, but as release frequency increases, supporting delivery at large-scale becomes complex and inefficient.
Learn more in our detailed guide to kubernetes ci cd and guide to kubernetes ci cd tools.
Spot introduced Ocean CD as part of the Ocean suite for Kubernetes to address the specific challenges of modern delivery release cycles. Ocean CD provides complete deployment and verification automation in one fully-managed solution, making it easy for users to execute deployments with high confidence. Key features of Ocean CD include:
Out-of-the-box progressive delivery strategies
Canary and blue/green strategies are easy to define, automate and customize. Developers commit code, use any CI tool and Ocean CD detects the deployments, automatically initiating the assigned rollout strategy.
Continuous verification automation
Ensure stability and quality of deployments even as release frequency increases. Routine verifications of deployments are conducted automatically and based on metrics from monitoring tools like DataDog and New Relic.
Automatic rollback
When issues are detected, Ocean CD initiates safe rollbacks and automatically tunes infrastructure to meet changing requirements of workloads. Continuous improvements are made to application deployments based on metrics collected during verification processes.
To learn more about Ocean for Continuous Delivery read our blog post or visit the product page.