What Is Google Cloud Pricing?
Google Cloud Pricing refers to the cost structure for using the Google Cloud Platform, a suite of cloud computing services. Google Cloud offers a wide range of managed services including compute, storage, and networking services. The pricing for these services can vary based on several factors such as usage, data storage, and computational power required.
Google Cloud provides different pricing models like the free tier, pay-as-you-go, Committed Use Discounts, and Spot Virtual Machines (VMs). Each pricing model is designed to suit different business needs, from short-term projects to long-term operations. Pay-as-you-go is the most expensive model, while other models offer varying degrees of discounts. The least expensive model is Spot VMs, which grant discounts of up to 91% compared to pay-as-you-go prices.
Understanding Google Cloud Pricing is critical for businesses transitioning their operations to the cloud. By understanding pricing and discount models, as well as cost analysis and optimization tools, organizations can significantly reduce costs and improve their operational efficiency.
In this article:
- Understanding Google Cloud Pricing Models
- Google Cloud Pricing for Computing Services
- Google Cloud Pricing for Storage Solutions
- Google Cloud Pricing for Networking
- Best Practices for Managing Costs on Google Cloud
Understanding Google Cloud Pricing Models
Google Cloud Free Tier
Google offers a Free Tier to new customers, giving them a chance to try out the services before committing financially. The Free Tier includes a 12-month free trial with $300 credit to spend on any Google Cloud services. Moreover, some services are always free, up to certain usage limits.
This model is great for startups and small businesses that are still exploring the potential of cloud services. It provides them with an opportunity to understand how Google Cloud works and assess if it fits their business requirements without any financial risk.
Pay-as-you-go
In the Pay-as-you-go model, you only pay for what you use. There are no upfront costs, and you can start or stop using services at any time without incurring additional costs. This model provides great flexibility, allowing businesses to scale their usage up or down based on their needs. However, it is also the most expensive way to use cloud services.
This model is ideal for businesses with fluctuating workloads. They can adjust their usage of cloud services as per their requirements and only pay for the resources they consume.
Committed Use Discounts and Sustained Use Discounts
Google Cloud also offers two main discount models: Committed Use Discounts and Sustained Use Discounts:
- Committed Use Discounts apply when you commit to using a particular service for one or three years. In return, Google Cloud offers significant discounts, often up to 57% off the regular price. This model is ideal for businesses with predictable long-term needs.
- Sustained Use Discounts, on the other hand, are automatic discounts that apply when you use a specific service for a significant part of the billing month. These discounts can be up to 30% off the regular price. This model rewards consistent usage and can be an excellent way to save money if you use resources on an ongoing basis.
When using committed or sustained use discounts, it is important to set up alerts and track your usage, to ensure that you are properly utilizing the discounted resources.
Spot VMs
Spot VMs are another way to save on Google Cloud. A Spot VM is a VM instance you can use at a significantly lower cost, between 60-91% off the regular price. However, these instances are not guaranteed and can be terminated by Google Cloud if the resources are needed elsewhere.
Spot VMs are ideal for fault-tolerant and flexible workloads that can withstand interruptions. They can be a cost-effective way to handle batch jobs, data processing tasks, and other non-critical workloads. With advances in cloud automation and cost optimization technologies, it is now also possible to use Spot VMs for mission critical workloads that cannot be interrupted.
Preemptible VM Instances
Preemptible VMs are an earlier version of Spot VMs, which are still offered by Google Cloud. They are similar to Spot VMs, with one primary difference: Preemptible VMs expire after 24 hours, while Spot VMs have no expiration time.
Google Cloud Pricing for Computing Services
Let’s now look at Google Cloud Pricing for some of its popular computing services.
Note: Cloud pricing is subject to change, and we cannot cover all the options offered by Google Cloud services. Consult the official pricing page for up-to-date pricing information. This also applies to the following sections.
Compute Engine
Compute Engine is Google Cloud’s Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) that lets you run workloads on Google’s physical hardware. It offers VMs that are highly customizable and can be adjusted to meet your specific needs.
The pricing for Compute Engine is mainly determined by the type of machine you choose and its running time. For instance, the cost per hour for an n1-standard-1 machine type in the US region is approximately $0.10. However, if you opt for a high-memory machine type like n1-highmem-2, the cost increases to around $0.20 per hour.
It’s also important to note that these prices are for on-demand instances. Spot VMs and committed use contracts offer substantial discounts.
It’s also worth noting that Compute Engine charges for other features like disk storage, network usage, and additional services like load balancing and cloud VPN. Therefore, you need to consider these factors when calculating the total cost.
App Engine
App Engine is Google Cloud’s Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) that lets developers build and host web applications. It handles the infrastructure management so that developers can focus on writing code without worrying about operations.
App Engine uses a flexible pricing model. You only pay for the actual resources your application consumes. The pricing depends on several factors, including instance hours, network egress, and database storage. For instance, in the standard environment, an F1 instance (the smallest instance) costs around $0.05 per hour, while a B4 instance (the largest instance) costs approximately $0.22 per hour.
App Engine also offers a free tier that includes free usage of up to 28 instance hours per day.
Google Kubernetes Engine
Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) is a managed service that allows you to run and manage containerized applications using Kubernetes, an open-source platform designed by Google.
The pricing for GKE is a bit more complex because it not only includes the cost of the Compute Engine instances but also a management fee for the Kubernetes master nodes. For example, the management fee for a standard cluster is around $0.10 per cluster per hour. However, this fee is waived for the first cluster in each zone. The cost of the worker nodes, on the other hand, is based on Compute Engine’s standard pricing.
Cloud Functions
Cloud Functions is Google Cloud’s Function-as-a-Service (FaaS) that lets developers write single-purpose functions that respond to cloud events without the need to manage a server or a runtime environment.
The pricing for Cloud Functions is based on the number of invocations, compute time, and network egress. For example, the first 2 million invocations per month are free, and beyond that, the cost is $0.40 per million invocations. Additionally, the compute time is charged at either $0.0000025 per GB-second (tier 1) or $0.0000035 per GB-second (tier 2).
Google Cloud Pricing for Storage Solutions
A major part of cloud costs is storage. We will look into the pricing of prominent Google Cloud storage solutions such as Cloud Storage, Persistent Disk, Cloud Bigtable, and Cloud SQL.
Cloud Storage
Cloud Storage is Google’s scalable, durable, and highly available object storage solution. The pricing model for Cloud Storage is based on the amount of data stored in your buckets and the network resources used when transferring data.
Each Cloud Storage class (Standard, Nearline, Coldline, and Archive) comes with its own pricing. For example, for the Standard class, you pay $0.020 per GB for the first 1 TB/month. As your usage increases, the price per GB decreases.
Beyond storage, other costs such as network egress, operations (like the retrieval of data), and early deletion fees (for Nearline, Coldline, and Archive classes) may apply.
Understanding your data usage patterns and how frequently you access your data can help you choose the right storage class and manage your costs effectively.
Learn more in our detailed guide to Google Cloud storage pricing
Persistent Disk
Persistent Disk is Google Cloud’s block storage solution. Persistent Disk is ideal for applications that require high-speed read and write operations to large datasets.
Pricing for Persistent Disk is straightforward and based on the provisioned size of your disks. There are two types of Persistent Disks: SSD (solid-state drives) and standard HDD (hard disk drives). The pricing for SSD Persistent Disks starts at $0.187 per GB/month, while HDD Persistent Disks start at $0.044 per GB/month. You are billed for the size of the Persistent Disk even if you aren’t using the full capacity.
Keep in mind that other costs, such as those associated with snapshot storage or network egress, may also apply.
Cloud Bigtable
Cloud Bigtable is Google’s NoSQL Big Data database service. It’s designed for the collection and retention of data from single-row transactions to petabytes of raw data.
The pricing for Cloud Bigtable is a bit more complex than the previous services. It’s based on the type and number of nodes in your cluster, the amount of storage used, and network egress. For example, the cost per node in the US is $0.72 per hour, and the cost for storage is $0.19 per GB-month.
Other costs can include storage (beyond the free allowance that comes with each node), network egress, and backups. Remember, Cloud Bigtable is designed for large operational workloads, so it’s crucial to understand your workload size and requirements to estimate your costs accurately.
Cloud SQL
Cloud SQL is Google’s fully-managed relational database service. Cloud SQL supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server.
Cloud SQL pricing depends on the database engine, instance type (shared or dedicated), and region. For example, the cost of a MySQL instance in the US starts at $0.0122 per hour. Pricing for dedicated instances is defined according to computing resources used, as shown in the table below.
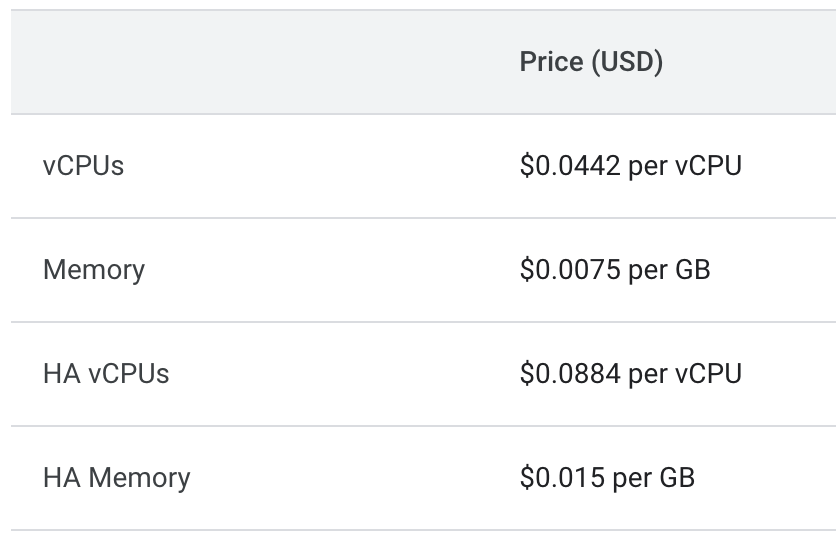
Source: Google Cloud
Other costs associated with Cloud SQL can include storage and networking. Keep in mind that automatic backups and any replicas are billed separately.
Learn more in our detailed guide to Google Cloud SQL pricing
Google Cloud Pricing for Networking
Virtual Private Cloud
Google Cloud’s Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) provides a secure and private network space for your cloud resources. It’s important to note that VPC itself is free; you only pay for the resources (such as VMs) that you run within the VPC.
However, the data transfer costs can add up depending on your usage. For instance, ingress data (data coming into your VPC) is usually free, while egress data (data going out of your VPC) is charged. The cost varies depending on the destination of the data.
For data transferred between zones in the same region, you pay $0.01 per GB. For data transferred between regions, the cost is $0.01 per GB within the US and $0.02 per GB in Europe (in other continents, cost is between $0.05 and $0.15 per GB).
For data transferred outside the Google Cloud (to the internet or a different cloud provider), the cost ranges from $0.045 to $0.085 per GB depending on the volume (Internet egress rates from the US, standard tier).
Content Delivery Network
Google Cloud’s Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed network of cache servers that deliver web content to users based on their geographic location. This service improves the speed and reliability of web service delivery.
When it comes to CDN pricing, you pay for the cache fill (data transferred from your origin servers to the CDN) and cache egress (data served to the users from the CDN). The pricing varies depending on the region. For example, in North America, cache egress is charged at $0.2 for the first GB, cache fill is charged at $0.04 for the first GB, and goes down to $0.02 and $0.01, respectively, as volumes increase.
HTTP(S) Load Balancing is required to use Cloud CDN, so you also need to consider its cost: $0.0075 per 10,000 requests. Additionally, any storage or compute resources used as your origin servers are charged at their respective rates.
Best Practices for Managing Costs on Google Cloud
Use Google Cloud Calculator
The Google Cloud Pricing Calculator is a free tool that lets you model your expected monthly bill using Google Cloud products. You can estimate your costs by choosing the products you plan to use, specifying their details, and setting your usage estimates. The calculator provides an interactive interface that helps you understand how different products and services will impact your overall costs.
Right-Size Resources
Right-sizing your resources means aligning your Google Cloud resources with your workload needs, ensuring you’re not overpaying for unused capacity.
To right-size your resources, start by monitoring your usage patterns and identifying where you might have over-provisioned resources. Once you identify these areas, you can scale down your resources to match your actual needs, resulting in significant cost savings.
Take Advantage of Committed Use Discounts
Committed Use Discounts are an important way to reduce your costs on Google Cloud, especially for workloads with predictable resource needs. However, before committing, make sure to analyze your long-term usage patterns and needs. Keep in mind that once you commit, you’re obligated to pay for the resources whether you use them or not.
Monitor and Adjust Based on Usage Patterns
Effective cost management on Google Cloud requires continuous monitoring and adjustment based on usage patterns. Google Cloud Platform provides various monitoring tools, such as Google Cloud Console, Cloud Logging, and Cloud Monitoring, to help you keep track of your resource usage and costs.
By regularly reviewing your usage data, you can identify patterns and trends that can inform your resource management decisions. For example, if you notice that certain resources are consistently underutilized, you can consider scaling them down to save costs.
Use Cost Management Tools and Follow Recommendations
Google Cloud offers a suite of cost management tools that can help you understand, control, and optimize your costs. These tools include cost reports, budgets and alerts, and recommendations on right-sizing and deleting idle resources.
One of the most effective ways to manage your costs is to set up budgets and alerts. This allows you to set a threshold for your spending and receive notifications when your costs approach or exceed this threshold. This proactive approach can help you avoid cost overruns and better manage your cloud budget.
Learn more in our detailed guide to Google Cloud costs
Optimize Google Cloud Costs with Spot
Google Cloud offers a myriad of options to build and scale your cloud infrastructure. As a result, however, the process of making sense of Google Cloud pricing can quickly become overwhelming even to skilled practitioners.
Spot offers a suite of tools to help you drive cost-efficiency in your Google Cloud environment. With Spot’s solutions, you can take advantage of Google Spot VMs, even for mission-critical applications, and simplify your Google Cloud infrastructure management. Learn more about Spot for Google Cloud.
