AWS is one of the primary providers for services that help users deploy and manage their containerized applications in the cloud. Since launching ECS in 2014 and EKS in 2017, AWS has learned a lot about running containers at scale and in production. In 2020, AWS developed Bottlerocket OS, a new operating system for hosting containers. This OS was specifically designed to address gaps left by the ECS and EKS-optimized AMIs, which are based on operating systems that run traditional software applications. Using Bottlerocket, customers benefit from enhanced security, more consistency in environments, and efficiency in operations.
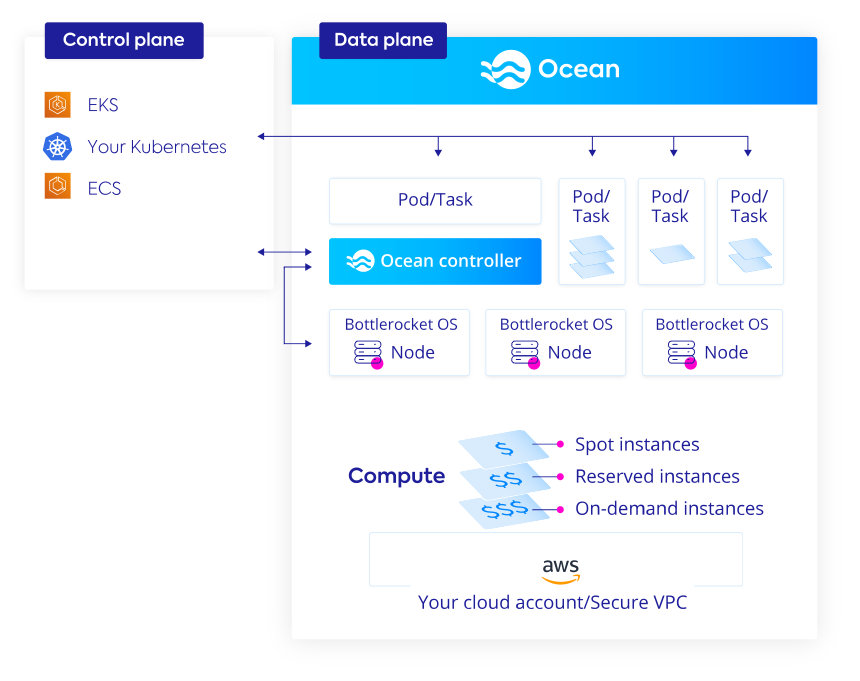
For our AWS customers, Spot Ocean supports the Bottlerocket OS, and now we’re excited to announce that Spot is a Bottlerocket OS Certified Provider. Spot Ocean customers can launch instances using the Bottlerocket OS, manage Bottlerocket OS nodes, and run the Spot controller on top of a Bottlerocket OS machine.
How does it work?
Bottlerocket is a free, open source, Linux-based operating system meant for hosting containers. It’s a slimmed-down OS that only includes what’s essential to run containers. This lean architecture helps to improve resource utilization and reduces the surface area that’s vulnerable to attack. It also enables automation of OS updates since this is done in a single step rather than package-by-package.
Spot Ocean runs seamlessly on top of Bottlerocket OS to automatically scale and manage nodes. Users can continue to leverage the cost optimization capabilities of Ocean that scale and provision spot instances, handle interruptions, and make efficient use of reserved instances.
Using Bottlerocket OS and Ocean
It’s easy to start using Bottlerocket OS with your EKS clusters running on Ocean or create new clusters running with Bottlerocket OS.
The following steps will guide you to configure your Virtual Node Group (VNG) to provision nodes in EKS clusters with Bottlerocket OS.
To use Bottlerocket OS in your EKS cluster managed by Spot Ocean, you need to provide:
- The latest ID of the Amazon EKS optimized Bottlerocket AMI for your EKS cluster version and region.
- User Data script to be used on a provisioned cloud VM to configure the instance and prepare it for joining the cluster.
Bottlerocket AMI
There are several options to get the latest ID of the Amazon EKS optimized Bottlerocket AMI for your EKS cluster version and region. You can retrieve the AMI ID with the AWS CLI or the AWS Management Console. In this example we will use AWS CLI. Please make sure you have AWS CLI installed and configured.
You can retrieve the image ID of the latest recommended Amazon EKS optimized Bottlerocket AMI with the following AWS CLI command. Replace 1.26 with your EKS cluster version and region-code with your EKS region for which you want the AMI ID:
aws ssm get-parameter –name /aws/service/bottlerocket/aws-k8s-1.26/x86_64/latest/image_id –region region-code –query “Parameter.Value” –output text
The example output can be as follows:
ami-0780e042609c1f433
Please note the shown value. We will use it in the VNG configuration step.
User Data Script
Bottlerocket OS uses a TOML-formatted configuration file as User Data. This includes the configuration of your EKS cluster.
Run the following command to generate the configuration file with the relevant cluster config, including the API endpoint and base64-encoded certificate authority. Replace region-code with your EKS region and cluster-name with your EKS cluster name. Please make sure you have eksctl installed:
eksctl get cluster –region region-code –name cluster-name -o json \ | jq –raw-output ‘.[] | “[settings.kubernetes]\napi-server = \”” + .Endpoint + “\”\ncluster-certificate =\”” + .CertificateAuthority.Data + “\”\ncluster-name = \”cluster-name\””‘ > user-data.toml
The command will create the user-data.toml file which will contain the User Data script. We will use this file’s content in the next step.
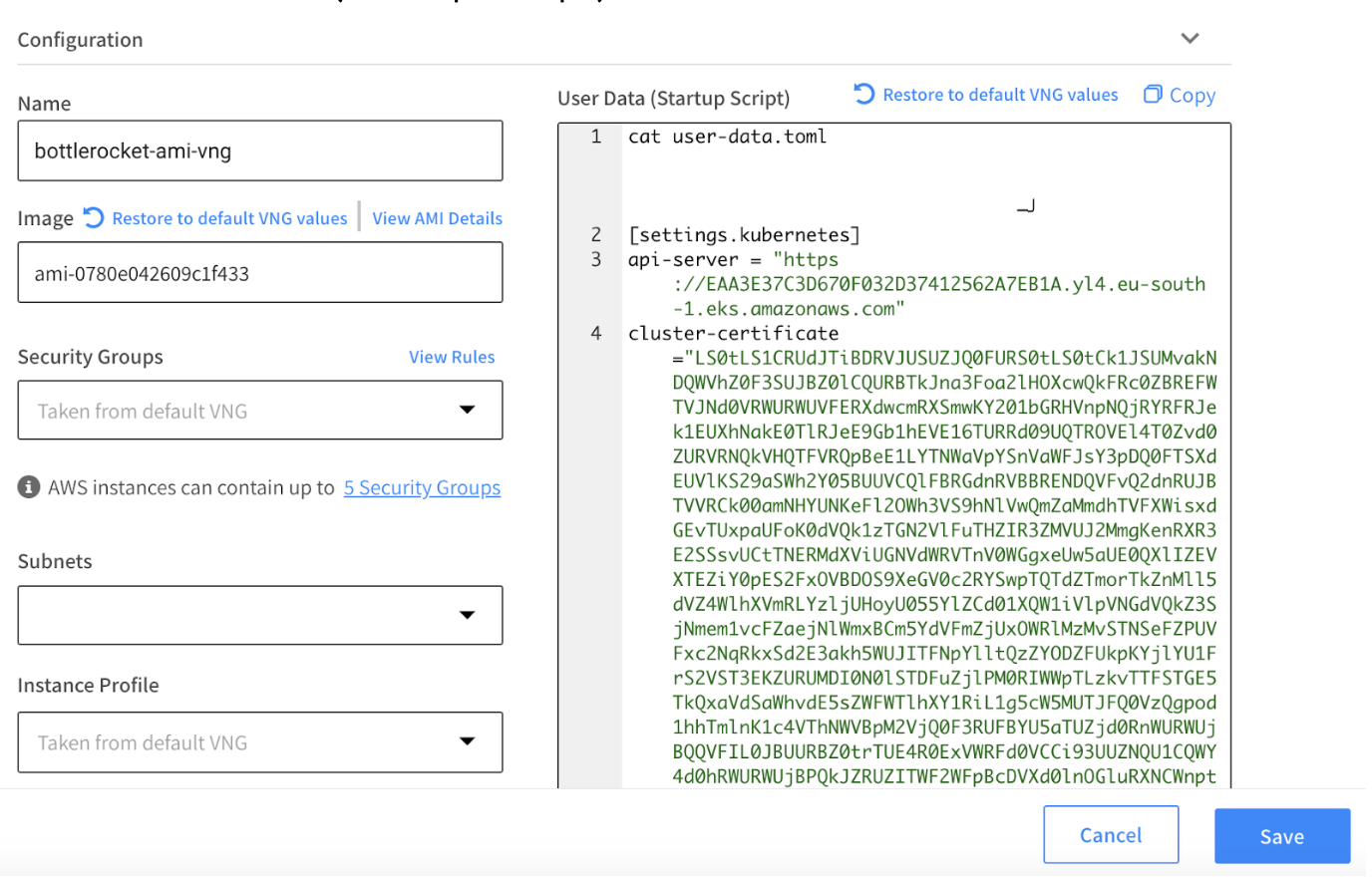
VNG Configuration
Navigate to the Virtual Node Group tab in the Spot Ocean web console. You can create a new VNG or edit the existing one.
In the configuration form:
- Insert Bottlerocket AMI you noted from the previous steps ID to Image field.
- Copy user-data.toml file content you created in the last steps and paste it to the User Data (Startup Script) field.
- Provide the rest of the required parameters in case you create a new VNG.
- Click save.
- If you edited the existing VNG please execute a cluster roll.
To learn more about Ocean and how you can get started with it, please review our documentation.